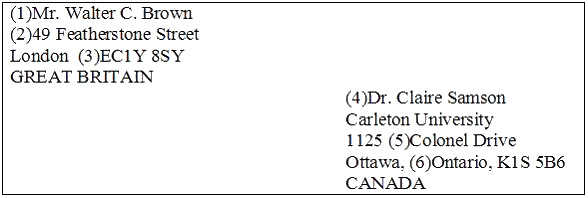Перед Вами конверт: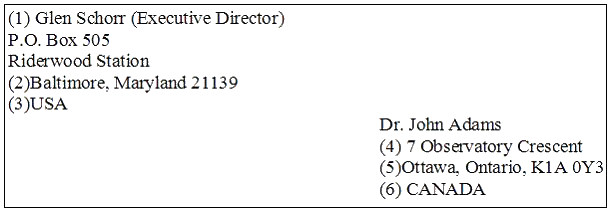
Соотнесите информацию под определенным номером на конверте с тем, что она обозначает.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания
Nanotechnology
1.Nanotechnology is the study of the controlling of matter on an atomic and molecular scale. Generally nanotechnology deals with structures of the size 100 nanometers or smaller in at least one dimension, and involves developing materials or devices within that size. Nanotechnology is very diverse, ranging from extensions of conventional device physics to completely new approaches based upon molecular self-assembly, from developing new materials with dimensions on the nanoscale to investigating whether we can directly control matter on the atomic scale.
2. Molecular nanotechnology describes engineered nanosystems operating on the molecular scale. Molecular nanotechnology is especially associated with the molecular assembler, a machine that can produce a desired structure or device atom-by-atom using the principles of mechanosynthesis.
3. In general it is very difficult to assemble devices on the atomic scale, as all one has to position atoms are other atoms of comparable size and stickiness. Another view, put forth by Carlo Montemagno, is that future nanosystems will be hybrids of silicon technology and biological molecular machines. Yet another view, put forward by the late Richard Smalley, is that mechanosynthesis is impossible due to the difficulties in mechanically manipulating individual molecules.
4. There has been much debate on the future implications of nanotechnology. Nanotechnology has the potential to create many new materials and devices with a vast range of applications, such as in medicine, electronics and energy production.
On the other hand, nanotechnology raises many of the same issues as with any introduction of new technology, including concerns about the toxicity and environmental impact of nanomaterials,and their potential effects on global economics, as well as speculation about various doomsday scenarios.
(Encyclopedia Wikipedia)
Выберите реплику, наиболее соответствующую ситуации общения.
Wife: «Could you do some shopping?»
Husband: «_______________».
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Solid
1. Solid is one of the major states of matter. It is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to changes of shape or volume. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire volume available to it like a gas does. The atoms in a solid are tightly bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice or irregularly one.
2. The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condensed matter physics (which also includes liquids). Materials science is primarily concerned with the physical and chemical properties of solids. Solid-state chemistry is especially concerned with the synthesis of novel materials, as well as the science of identification and chemical composition.
3. The forces between the atoms in a solid can take a variety of forms. For example, a crystal of sodium chloride (common salt) is made up of ionic sodium and chlorine, which are held together by ionic bonds. In diamond or silicon, the atoms share electrons and form covalent bonds. In metals, electrons are shared in metallic bonding. Some solids, particularly most organic compounds, are held together with van der Waals forces resulting from the polarization of the electronic charge cloud on each molecule. The dissimilarities between the types of a solid result from the differences between their bonding.
Перед Вами конверт.
Соотнесите информацию под определенным номером на конверте с тем, что она обозначает.
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания
Nanotechnology
1.Nanotechnology is the study of the controlling of matter on an atomic and molecular scale. Generally nanotechnology deals with structures of the size 100 nanometers or smaller in at least one dimension, and involves developing materials or devices within that size. Nanotechnology is very diverse, ranging from extensions of conventional device physics to completely new approaches based upon molecular self-assembly, from developing new materials with dimensions on the nanoscale to investigating whether we can directly control matter on the atomic scale.
2. Molecular nanotechnology describes engineered nanosystems operating on the molecular scale. Molecular nanotechnology is especially associated with the molecular assembler, a machine that can produce a desired structure or device atom-by-atom using the principles of mechanosynthesis.
3. In general it is very difficult to assemble devices on the atomic scale, as all one has to position atoms are other atoms of comparable size and stickiness. Another view, put forth by Carlo Montemagno, is that future nanosystems will be hybrids of silicon technology and biological molecular machines. Yet another view, put forward by the late Richard Smalley, is that mechanosynthesis is impossible due to the difficulties in mechanically manipulating individual molecules.
4. There has been much debate on the future implications of nanotechnology. Nanotechnology has the potential to create many new materials and devices with a vast range of applications, such as in medicine, electronics and energy production.
On the other hand, nanotechnology raises many of the same issues as with any introduction of new technology, including concerns about the toxicity and environmental impact of nanomaterials,and their potential effects on global economics, as well as speculation about various doomsday scenarios.
(Encyclopedia Wikipedia)
How is it possible to produce a desired structure or device on an atomic scale?
Look _______ through the notes before you start writing.
Выберите реплику, наиболее соответствующую ситуации общения.
A.: «Could you show me the way to the nearest hotel?»
B.: «__________________».
Прочитайте текст и выполните задания.
Light
1. The form of energy that illuminates our world is called light. It usually comes from hot objects, like the sun or fire, but it is also produced by electricity and some chemical reactions. Light is the only part of the electromagnetic spectrum (which includes microwaves, ultraviolet rays, and X-rays) that is invisible to the human eye. It travels at 186,000 miles (300,000 km) per second, and nothing can travel faster. Like other forms of energy, light travels in waves, but it can also travel in packets of energy called quanta. This enables it to travel through a vacuum.
2. Light rays are reflected when they hit a shiny or silvered surface, such as a still pool of water or a mirror. Reflection involves two light rays: the incoming ray and the reflected ray which bounces off the reflecting surface. The two rays are at identical angles to the reflecting surface on either side of an imaginary line.
3. Refraction is a property of all types of energy that travel in waves, including light. Light waves normally travel in straight lines, but when they pass from one transparent material to another, they usually refract, or bend. Refraction occurs because light travels at different speeds in different materials. As light from a material with a low density, such as air, enters a material with a high density, such as water, its speed is reduced. This causes it to bend (except when it enters a material at a right angle).
Перед Вами конверт.
Соотнесите информацию под определенным номером на конверте с тем, что она обозначает.